Power lines and interfacing in a computer
Download free latest unlimited KCSE revision papers @ www.manyamfranchise.com
Author: Atika M. Nyamoti
FireWire is the newest and fastest serial computer port
(bus) known also as i.Link (Sony) or IEEE-1394 by its technical name. It was
developed by Apple and Texas Instruments mainly for use with video and audio
demands in both Macs and PCs, but can be used for connecting many different
peripherals. It reaches speeds of 400mbits/sec or even more in newer versions.
FireWire is an Apple trademark but it has become the more commonly used name
referring to IEEE-1394. It has 6 pins. The female or socket in the computer has
a rectangular shape and the connector that goes on the peripheral is round. It
has the capability of "hot plugging" which is the ability for
plugging and unplugging a device without powering down. In many ways has come
to replace SCSI as an
external port. There are still only few motherboards that come with a FireWire
port, being more common in Mac computers
Author: Atika M. Nyamoti
Power lines and interfacing in a computer
An interface is a tool and concept that refers to a point of interaction between components, and is applicable at the level of both hardware and software. Most computer interfaces are bi-directional, but the mouse or graphics adapter are uni-directional. |
| interfacing |
Hardware Interfacing
-Hardware interfaces exist in computing
systems between many of the components such as the various buses, storage
devices, other I/O devices, etc. A hardware interface is described by the
mechanical, electrical and logical signals at the interface and the protocol
for sequencing them (sometimes called signaling)
– This refers to
connecting a peripheral device to a computer through ports using either cables
or wireless connectivity.Peripheral devices interfacing
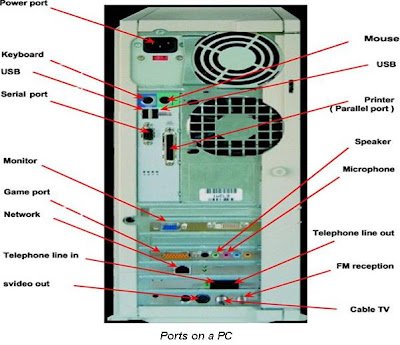 |
| Ports at rare view |
Parallel Interface
Parallel cables transmit
information simultaneously using a set of many conductors (wires). The
advantage of using such cables is that they transmit data faster over a short
distance.
A parallel cable connects to a parallel interface port
commonly referred to as line printers (LPT). Parallel cables are used to
connect printers, optical scanners and some removable storage devices such as a
zip drive.
 |
| parallel cables |
Serial interface
Serial ports also known as COM or RS232 ports, support
transmission of data one bit at a time, hence it is slower than the parallel ports,
However they are good than parallel cables because they can transmit data over
a larger distance. They are used to connect devices such as the mouse and some
printers.
 |
| serial cables |
COM
Is not an acronym unlike many of
the other ports; it simply stands for the "com" in communications. It
is commonly known as the serial port because it was the first port to use that
type of communication. Widely used since personal PCs became a common tool. Are
cheap and can be used with longer cables than parallel ports. Like the LPT port
it is shaped like a trapezoid, but smaller, with the short end in the bottom
and has 9 pins divided in 2 rows, one with 5 and other with 4 (be careful not
to confuse it with the monitor port which is similar in size and shape but it
has more pins and it is used only for monitors.) Commonly used to connect the
mouse, keyboard, modems, cameras, and PDAs, especially before USB ports
appeared. There are usually more than one COM ports in a computer and to
differentiate them they are labeled with a number after COM. Commonly there are
COM 1 and COM2 available. A typical COM port reaches speeds of 115Kb/sec.
Advantages-COM ports are very versatile. Many types of peripherals have used the COM port traditionally. Though, with the advent of USB, the use of COM ports is dwindling.
Advantages-COM ports are very versatile. Many types of peripherals have used the COM port traditionally. Though, with the advent of USB, the use of COM ports is dwindling.
Common Peripherals-As mentioned
above, COM ports are extremely versatile. They have be used to connect mice,
keyboards, modems, cameras, and PDAs, to name a few.
USB-Universal Serial Bus
is a serial and female port that can be use for any peripheral available in both Macs and PCs. It is one of the newest and faster computers available. It is slower than a FireWire port but is more than adequate for the type of peripherals for which it was designed for. In many ways have come to replace the standard parallel (LPT) and Serial (COM) ports, including printer, keyboard and mouse ports, having a much faster communication capabilities. Its speed goes upto 12 mbits/sec. The socket (and proper plug) in the computer has the shape of a thin a rectangle (called "Series A") measuring about 1/2 inch by 1/8 inch and are usually located on the back of your computer. Some computers also have USB ports located on their fronts (MAC in the side). When given a choice, it is suggested that the ports on the back be used so the ones in the front are available to plug a mobile device like a camera.
Advantages: It has the
capability of "hot plugging" which is the ability for plugging and
unplugging a device without powering down. Now there are many motherboards that
came with 2 USB ports available, being common in both Mac and PCs. USB devices
are self-identifying, and USB is Plug-and-Play compliant, which means that
installation and configuration of USB peripherals will be relatively easy. USB
cables also carry power, so you don't need extra cables or transformers. · USB
ports on your computer will work with any USB peripheral that you want to plug
into it. USB is also "hot-swappable": you can plug stuff in or out
without turning off the computer. One
disadvantage is that is has to use a Windows98 or higher operative system
and Windows NT doesn't support USB.
Common Peripherals: Even
though USB supports any peripheral so far the most common ones that come with a
connection for these ports are printers, digital cameras and mice.
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI)
SCSI stands for "Small
Computer System Interface" and is usually known by the way it's pronounced
"scuzzy". It's a general-purpose male and parallel port for
connecting many different devices to a computer. It's a fast port that was
available before USB and FireWire. Usually used with CD-ROM drives and
scanners. Commonly present in older Macs, if you want to use it on a PC they
require an additional card that rarely comes on a regular PC. A common SCSI
port reaches between 5 and 10 mbits/sec. SCSI usually is more used in big
computers like servers and mainframes. When it is used in desktop PCs it is
because you can add a scanner and several other drives (CD, DVD or Zip drives)
to one SCSI cable chain. However this is less important now that alternate
multi purposes flexible ports such as USB and FireWire are more popular.
 |
| SCSI |
Advantages: SCSI ports are
very fast and could in theory be used with any peripheral and with many of them
at the same time. However really they are used mostly for scanners and external
drives especially on Macs and big PC servers.
Disadvantages-One of the problems is that there is not a real
standard for manufacturers so there are some different types of SCSI ports in
the market. Also they are quiet expensive and so are the peripherals, cables
and adapters associated with it. That is why they are more common in
professional setting rather than for home use.
Common Peripherals: Even
though theoretically they could be used with almost peripheral they are
commonly used with scanners and external drives.
Personal System 2 (PS/2) Interfaces
PS2 is a port that was specially designed to use with mice and keyboards. It is also known as the standard mouse port. It's circular in shape about 1/2" and has six metal pins on the inside (Not to confuse with the old keyboard 5 pin bigger round connector.) This type of connection is common on all computers since 1997 and among other things it can serve to the purpose of freeing up a COM port to be used with other devices.
Advantages -PS2 ports are
always available in every computer. And it is fairly cheap compared to other
ports. It is especially standardized for mice and keyboards.
Common Peripherals: Mice and
Keyboards are commonly connected to computers by PS2 ports.
Audio Interface-Audio interface is used to connect speakers and
microphone.
Fire wire Interface
 |
| Fire Wire Cable |
Advantages FireWire transmits data very fast
(400mbits/sec or more). FireWire is also capable of "hot plugging",
which allows users to plug and unplug peripherals without restarting their
computers.
Common
Peripherals Currently FireWire is almost entirely used to connect digital
video cameras to computers, though it is possible that many more audio and
video media will utilize FireWire in the near future.
LPT
LPT (line print terminal or local printer terminal) is commonly known as the parallel port and typically used as the printer connection device. It can transmit signals for distances limited to 20 feet or less. It’s Faster than serial COM ports but more expensive. A typical LPT port reaches a speed of 150kb/sec. There can be more than one LPT ports in a computer and to differentiate them they are labeled with a number after LPT. It is most common to have only one for the printer called LPT1. It is shaped as a trapezoid with the short end in the bottom and 2 rows of pins, one 13 and other with 12 pins.
Advantages-It
is faster than serial ports. It is available in every computer. Also, it is a
port that is specially standardized for a printer to connect to a computer.
Common Peripherals-Commonly
a printer uses LTP1 port.
Wireless peripheral interface
A wireless peripheral interface is used for coupling with a Universal Serial Bus (USB) port for connecting a wireless peripheral with a host computer or controller. Wireless peripheral devices (e.g., keyboard, mouse, trackball, touch pad, joysticks, and game controllers) transmit communication signals, e.g., radio frequency (RF) signals, to the peripheral interface, which are received and processed into formats suitable for transmission to the host computer or controller via USB, either alone or in combination with other standard external bus systems, such as serial and PS/2. Other technologies for wireless interface include: Bluetooth, Wi-Fi (derived from playing with words I.e. from Hi-Fi which stands for high fidelity) and Infrared.
Infrared is a wireless interface that uses infrared to connect to
infrared-enabled devices. Bluetooth
is also a wireless interface that uses short-range radio broadcast to connect
to any Bluetooth-enabled device.
Basic computer setup cabling
Before attempting to carry any setup activity, the following
precautions should be observed:
1) Disconnect
all drives from power source before starting to work on them.
2) Do
not work on peripheral device without the guidance of a teacher.
3) Never
work alone because, you may need help incase of an emergency.
4) Discharge
any static electricity that might build upon the hands by touching an earthen
metallic object and then wearing an antistatic wrist member. This is because your body can hold as much as 200
volts of static charge that can damage sensitive components on the mother
board.
5) Avoid
touching metal conductors with wet hands. This may cause short circuiting thus
damaging chipsets.
6) Don’t
force a component to open/eject. There are laid procedures for every
opening/ejection. Force can break or destroy a component makeup.
Tools and other
requirements
The following tools
are necessary in any setup:
- Screw drivers
- Antistatic wrist member
- Pliers
- Devices manual
- Devices software (drivers)
- Fuse testers
- Gloves etc
Mounting internal
devices
External devices are connected to the motherboard via
special sockets known as ports whilst
internal devices are connected through slots
and sockets. It’s recommended to
study the manufacturer’s manual before connecting devices.
Mounting hard drives
and optical drives
Internal devices are connected to the motherboard using
special ribbon cables. Hard disks and optical drives are connected to the
motherboard through interface connectors commonly referred to as controllers.
Three types of controllers are:
- Ø EIDE- enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics
- Ø SCSI- Small Computer Systems Interface
- Ø SATA- Serial Advanced Technology Attachment
EIDE are more efficient and supports hot-swapping. Hot-swapping means that a drive can be removed or
inserted while the computer is still on. Each EIDE supports up to two drives on
a single ribbon cable. This type of setup is called a master/slave configuration because one controller directs the
activities of both drives. To mount an EIDE drive, proceed as follows:
- Wear antistatic wrist member to discharge any static charge on the body.
- Determine which drive will be the master and use the drive label information to determine which jumper settings to use for a master or a slave.
- Check that a free drive bay is available, slide the disk into that bay and screw it into place.
- Ensure that there is free power connector from the power supply unit and connect it to the drive. Notice that it is designed to fit in its socket in only one direction.
- Identify pin 1 as labeled on the drives socket and match it with the red or brown continuous line of the ribbon cable. Most cables will only fit in one direction.
- Connect the interface cable to the drive, then into the controller slot on the motherboard.
- If installation is complete, replace the casing power.
Connecting external
devices
To connect a device to the system unit, you need to identify
its port and interface cable.
- Gently and carefully connect the interface cable of each device to the correct port and to the device if it is not already fixed permanently.
- Connect the computer to the power source and switch it on.
- Observe boot up information on the screen to see whether Power-On-Self-Test (POST) displays any error message.
- A successful boot means that the computer was properly set up
Group Discussion for Revision questions on topics
- What are:
- input devices
- processing devices
- output devices
- Discuss the following terms
a. data
b. information
- Name four main parts that make up a computer
- What are peripheral devices?
- Name such devices in question 4 above
- With the aid of an organizational chart, show how computers are classified.
- In which classification do the school computers belong? Why?
- Discuss classification of computers according to:
a. Size
b. Purpose
c. Functionality
- With an aid of a diagram show how digital and analogue signals are represented.
- Name at least six microcomputers available in the Kenyan market today.
- Name 10 areas where computers are used and what they are they used for?
- What are the main functions of a computer?
- What is the main purpose of a computer?
- Briefly discuss evolution of computers since ages before Christ to date?
- Discuss causes of computer damage in the computer lab and how to avoid them?
- List six safety precautions in the computer lab. Why are they necessary?
- Discuss classification of keyboard keys and give examples for each classification.
- Draw symbols for each keyboard key listed below and indicate their uses?
a. SysRq
b. Escape
key
c. Spacebar
d. Backspace
e. Home
f. End
g. Insert
h. Tab
Key
i.
Shift key
j.
Control
k. Num
Lock
l.
Caps Lock
m. Scroll
Lock
n. Windows
logo key
o. Menu
Key
- Indicate whether the following devices listed below are pointing, scanning or keying devices.
a. Joy
Stick
b. Keypad
c. Flatbed
d. MICR
e. Keyboard
f. Mouse
g. Trackball
h. OBR
i.
OCR
j.
Stylus
k. Light
pen
l.
Touch screen
m. Camera
- …………………is regarded as the brain of the computer and also known as a microprocessor.
- Using an organizational chart, show parts of the Microprocessor.
- ………………..is used to input voice in the computer.
- By the use of a well labeled diagram, show all the events that ‘task A’ go through to be processed into information.
- This is a gadget mounted on the motherboard, drives or HDD used as a ROM, hosts a number of other electrical gadgets like capacitors, resisters and transistors. Even the microprocessor belongs to this gadget. What is this gadget?
- Kwamboka went into a shop to buy a RAM for her desktop computer and she encountered problems in interpreting the following abbreviations: DDR, SDR, DIMM, SIMM, SRAM and DRAM. Can you help her understand these terms?
- Differentiate between a computer, a system and a computer system.
- The speed of a computer is measured by the frequency of computers processing signals. True/false? If true, explain how?
- Draw a well labeled diagram for:
a. HDD
b. HDD-disk
platter
- Name six softcopy display devices available in the Kenyan market today. How do they differ from each other?
- Discuss:
a. Pixel
b. Color
depth
c. Resolution
d. Refresh
rate
e. Display
size
- By the use of organizational chart, discuss classification of printers.
- ……………… is a special type of printer used to produce bill boards, engineering drawings, maps etc
- Discuss:
a. RAM
vs. ROM
b. Firewire
vs. USB
c. PS/2
vs. Wireless
d. SCSI
vs. Firewire
e. COM
vs. LPT
- Disconnect all computer parts and reassemble them again. Write a report on every activity observed. The report should feature:
a. Tools
used
b. Safety
precautions observed
c. Disconnecting
procedure
d. Procedure
for connecting the CPU, HDD, Drives, Cards, CMOS battery, peripheral devices
and which interface was used to connect
which device
e. A
successful booting procedure.
- Discuss numerous factors to consider when purchasing a printer.
- Nyambura bought a brand new desktop computer with a warranty but upon reaching home, the computer could not boot. List numerous reasons that may have caused the computer not to boot. What will you advice her to do if the computer failed completely to start?
- discuss:
a. Wi-FI
vs. Bluetooth
b. Keypad
vs. Keyboard
c. SMS
vs. MMS
d. Memory
Card vs. Flash Disk
e. CD
vs. LS Super Disk
f. Optical
Tape vs. Optical Card
g. Gramophone
Disk vs. DVD
h. Live
disk vs. HDD
- Discuss and analyze all video adaptors
- what are these devices used for:
a. LED
b.
Speakers
- What are the advantages of tower computers over desktop computer models
- Give reasons who mobile phones are regarded as computers







Comments
Post a Comment
Talk about this Post: